
A distinctive neural signature found in the brains of people with dyslexia may explain why these individuals have difficulty learning to read, according to a study from MIT neuroscientists.
The researchers discovered that in people with dyslexia, the brain has a diminished ability to acclimate to a repeated input — a trait known as neural adaptation. For example, when dyslexic students see the same word repeatedly, brain regions involved in reading do not show the same adaptation seen in typical readers.
This suggests that the brain’s plasticity, which underpins its ability to learn new things, is reduced, says John Gabrieli, the Grover M. Hermann Professor in Health Sciences and Technology, a professor of brain and cognitive sciences, and a member of MIT’s McGovern Institute for Brain Research.
“It’s a difference in the brain that’s not about reading per se, but it’s a difference in perceptual learning that’s pretty broad,” says Gabrieli, the study’s senior author. “This is a path by which a brain difference could influence learning to read, which involves so many demands on plasticity.”
Former MIT graduate student Tyler Perrachione, now an assistant professor at Boston University, is the study’s lead author, which appeared in the Dec. 21 issue of Neuron.
Reduced plasticity
The MIT team used magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) to scan the brains of young adults with and without reading difficulties as they performed various tasks. In the first experiment, the subjects listened to a series of words read by either four different speakers or a single speaker.
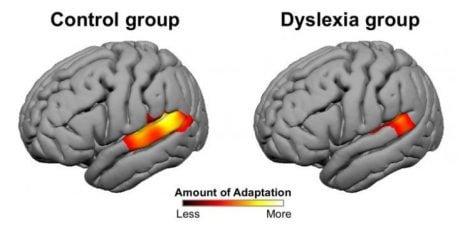
The MRI scans revealed distinctive patterns of activity in each group of subjects. In non-dyslexic people, areas of the brain involved in language showed neural adaption after hearing words said by the same speaker, but not when different speakers said the words. However, the dyslexic subjects showed much less adaptation to hearing words said by a single speaker.
Neurons that respond to a particular sensory input usually react strongly at first, but their response becomes muted as the input continues. This neural adaptation reflects chemical changes in neurons that make it easier for them to respond to a familiar stimulus, Gabrieli says. This phenomenon, known as plasticity, is key to learning new skills.
“You learn something upon the initial presentation that makes you better able to do it the second time, and the ease is marked by reduced neural activity,” Gabrieli says. “Because you’ve done something before, it’s easier to do it again.”
The researchers then ran a series of experiments to test how broad this effect might be. They asked subjects to look at series of the same word or different words, pictures of the same object or different objects, and pictures of the same face or different faces. In each case, they found that in people with dyslexia, brain regions devoted to interpreting words, objects, and faces, respectively, did not show neural adaptation when the same stimuli were repeated multiple times.
“The brain location changed depending on the nature of the content that was being perceived, but the reduced adaptation was consistent across very different domains,” Gabrieli says.
He was surprised that this effect was so widespread, appearing even during tasks that have nothing to do with reading; people with dyslexia have no documented difficulties recognizing objects or faces.
He hypothesizes that the impairment shows up primarily in reading because deciphering letters and mapping them to sounds is such a demanding cognitive task. “There are probably few tasks people undertake that require as much plasticity as reading,” Gabrieli says.
Early appearance
In their final experiment, the researchers tested first and second graders with and without reading difficulties, and they found the same disparity in neural adaptation.
“We got almost the identical reduction in plasticity, which suggests that this is occurring quite early in learning to read,” Gabrieli says. “It’s not a consequence of a different learning experience over the years in struggling to read.”
Gabrieli’s lab now plans to study younger children to see if these differences might be apparent even before children begin to learn to read. They also hope to use other types of brain measurements, such as magnetoencephalography (MEG), to follow the time course of the neural adaptation more closely.

